Online Learning Portal
Online Learning Portal

Indian culture is a diverse topic. It encompasses cultural aspect from ancient, medieval to modern times. Coming to questions from this section, aspirants finds them difficult to solve. There are many reasons for this. Quite understandably culture is quite factual and not an easy to prepare. Moreover, it has unending aspects to be covered that is beyond anyone’s capability. Again, the best way to prepare is from analysis of past year papers and following a simple strategy. What can be a simple strategy if the subject is tough ?
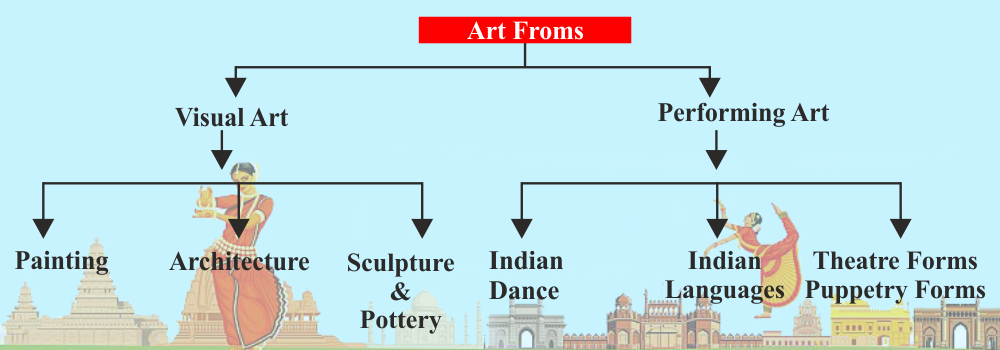
Indian culture comprises of Art, Architecture and Literature. Almost every single book available in the market will explain in length and breadth about the syllabus and domains. To tell you frankly even if you memorize everything, you cannot solve the questions as some of them are analytical. Hence, the very purpose of this article here is to create an easy mind map for your preparation.
All you have to do is be selective in reading the books. Following the strategy given here will make sure that you have prepared culture without much difficulty. Also, a standard source to prepare culture is Current Affairs.
Since this section, overlaps with Ancient, Medieval and Modern History, you will see certain topics repeated here.
From Mauryan Empire the developments in the above field became prominent.If we start dividing and covering each and every ruler’s domains based on them, then we will end up writing a book that we definitely don’t want. Let us make it simple.
RATHER, YOU CAN JOIN ASPIRE IAS CRASH COURSE OF CULTURE TO EASILY LEARN CULTURE FOR UPSC EXAM, WITHIN THE CLASS ITSELF. ALL QUESTIONS IN THE LAST 5 YEAR WISE FROM THIS CLASS ONLY.
Focus:
focus
focus
focus
focus
focus
Note: In 2014, UPSC asked more questions based on locations and terms. You should be prepared to handle such questions. Do not read extensively, just focus on few aspects that we mentioned above like Locations, Features, Similarities and dissimilarities etc. Nobody can remember everything. Try to make your learning simple.
This can be broadly divided into Indian Music forms, Folk Music, Dance forms, Martial Arts, Tribal Arts, Languages, Theatres, Puppetry and traditional activities
focus
Example: Silambam is a weapon-based Indian martial art from Tamil Nadu. The term silambambu referred to a particular type of bamboo from the Kurinji hills in present-day Kerala. Thus silambam was named after its primary weapon, the bamboo staff.
Famous Tribal and Folk Arts: Folk music and Communities associated.
Example: The Manganiar and related Langha caste are Muslim communities in the desert of Rajasthan, India. They are famous for their classical folk music. They are the groups of hereditary professional musicians.
Example: Bhand Pather, the traditional theatre form of Kashmir, is a unique combination of dance, music and acting. Satire, wit and parody are preferred for inducing laughter. Bhand Pather are mainly from the farming community, the impact of their way of living, ideals and sensitivity is discernible.
Example: The string puppets of Karnataka are called Gombeyatta. They are styled and designed like the characters of Yakshagana, the traditional theatre form of the region. The Gombeyatta puppet figures are highly stylized and have joints at the legs, shoulders, elbows, hips and knees. Episodes enacted in Gombeyatta are usually based on Prasangas of the Yakshagana plays. The music that accompanies is dramatic and beautifully blends folk and classical elements.
Note: Try to find relevant issues from newspaper and prepare it from there as well. This way on daily basis, you will be in touch with culture.
Indian Languages– Classical language; recently, few languages were added to the category of classical languages, so UPSC asked a question in 2014.
Theatre and Puppetry forms – not every form is important, if there is any news regarding a particular form read about it.
focus
focus
Note: Tribal arts and traditions are regularly in news. The Hindu has a separate section on it where articles on Music, Dance, Traditions, Art and Culture of specific era are regularly updated. You should focus on them but smartly, since reading the entire article is ‘not’ relevant from the exam perspective.
Note: While preparing from texts, focus on such terms and make a list of it. Keep on revising them.

Our Popular Courses
Module wise Prelims Batches
Mains Batches
Test Series